By Shawn Butterworth
Guest Writer for Wake Up World
There are two types of electrolyzed water: one is alkaline water and the other is acidic water. And each is produced from ionizing tap water with an alkaline water machine.
Each type either has a positive ORP or a negative ORP (Oxygen Reduction Potential) value. Through the process of electrolysis, the two water types that are produced are: electrolyzed reduced water, and electrolyzed oxidized water; the reduced water is the alkaline water, and the oxidized water is the acidic water. These devices that do the electrolysis are referred to as alkaline water machines, because it is the alkaline water that people are mostly interested in for drinking purposes.
The electrolyzed reduced alkaline water primarily has an ORP measurement on average of between -500 to -800 mV. With this value, through studies that I will reference in this article, it has the ability to scavenge for ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species, otherwise known as toxins or free-radicals). Also, pH (which stands for power of hydrogen) levels of reduced water measure in most cases in between 8 to 10. With the higher pH level after ionization, this is why it is called alkaline water.
On the other hand, the electrolyzed oxidized acidic water consists of an ORP value between +500 to as high as +1300 mV. Having this value enables it to effectively destroy bacteria and pathogens in seconds with contact. As this water has efficient cleaning effects, it is widely used in Asian countries as a safe alternative to conventional cleaners. The pH value of electrolyzed oxidized water can measure anywhere from 4 to 2.5. But in order to effectively remove pathogens within seconds, it must be as close to 2.5 as possible.
When you understand the uses of the acidic water as well as alkaline water, you can get a lot more value from a water electrolyzer.
[pro_ad_display_adzone id=”110028″]
How electrolyzed water is produced
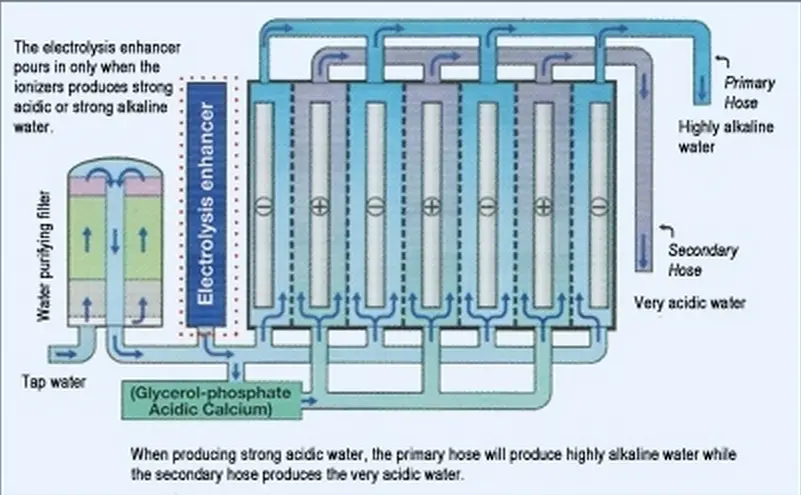
Tap water which undergoes a process known as ‘electrolysis’, is split into acidic oxidizing water and alkalized reduced (anti-oxidizing) water. A cell composed of an anode and a cathode is required to have an electrical current, thereby causing the separation effect.
During the electrolysis process, the cathode which has the negative charge attracts the oxidizing water, whereas the anode attracts the reduced alkaline water. After going through the input (faucet hose), once the tap water has been fully ionized, each water then exits through an individual output hose.
The alkaline water, which has a higher concentration of OH – hydroxyl ions – attracts to the positive charged anode through opposite attractions. Whereas the strong acidic water is less abundant in hydrogen.
Below shows a diagram in that will explain how tap water was is electrolyzed as it processes through an alkaline water machine cell chamber.
This technology was first introduced to the world in the 1940s, when German scientists wanted to replicate a special water of water that is found in certain water springs that are extremely popular around the world. These springs were referred to as “healing springs”, and a few of them were located at Tlacote el Bajo Mexico, Nordaneau Germany, and Lourdes France. The similarity between reduced alkaline water and the water at these springs are identical. The primary property of the water is of having the anti-oxidant potential, otherwise known as the ‘reducing effect’… being able to reduce the oxidization or aging process.
Electrolyzed water, also referred to as reduced alkaline water or acidic oxidizing water, was approved by the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare in the year of 1965. It has been demonstrated, through double blind testing, that it is effective and safe for health issues such as: abnormal intestinal fermentation, chronic diarrhea, constipation, antacid, and dyspepsia. In addition, it has been demonstrated that electrolyzed reduced water can scavenge ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) and can protect the DNA. [1]
Uses for electrolyzed water
- ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species, or “Free Radicals”) scavenging ability.
- Therapeutic and preventative effect on various diseases.
- Washing capability.
- Sterilizing effect.
- Anti-bacterial agent.
- Effective deodorization.
- Acid soil improvements.
- Compost maturation acceleration.
- Enhanced resistance of plants against stress from oxygen.
- A reduced deterioration and rot of foods.
- Seed sterilization.
- Enhanced preservation of cut flowers. [1]
Summary of clinical health improvements from the intake of reduced water
- Diabetes mellitus blood glucose levels improvement.
- Uric acid levels in gout reduction.
- Health improvements of liver function related conditions such as cirrhosis of liver, hepatitis, and hepatic disease.
- Noticeable improvement of ulcers and reduction of recurrences.
- Improvements related to reduced cholesterol levels and hypertension.
- Reduction of rheumatism collagen disease and autoimmune disorders.
- Enhancements of recovery related to ‘so called specific diseases” including ulcerative colitis, Kawasaki’s disease, Behcet’ syndrome, Chrohns disease.
- Improvements related to malignant liver tumors, metastic, and hepatoma tumors reduction.
- Reduction in conditions such as chronic constipation, diarrhea, and general malaise.
- Improvements related to hyperbilirubinemia in newborns.
- Experiences improvements in relation to pregnant women; smooth delivery, enough lactation, almost no emesis, and satisfactory growth of newborns. [2]
Slow the aging process with electrolyzed water
Through studies, it has been found that electrolyzed/reduced water can scavenge for oxygen reactive species, and is able to act as a powerful anti-oxidant. [3] Alkalized water has a negative ORP (oxygen reduction potential) value, causing it to have an anti-oxidizing ‘reducing’ effect. This effect primarily reduces the amount of oxidation caused by free radicals and toxins. As toxins enter into the body, they will steal a free-electron from a healthy tissue or cell, if it is not neutralized by anti-oxidants.
In Japan, when a substance has a negative ORP of -300 or less, it is considered a medicine. That is why alkaline water machines are found in hundreds of Japanese hospitals and medical centers.
By neutralizing more of these toxins, rather than them ‘oxidizing’ healthy cells in the body, it can reduce the oxidation process of the body. Therefore by reducing the oxidation it can slow the aging process. Also, another benefit from these anti-oxidants, it can reduce DNA damage that can be associated with free radical damage. [4] In addition to DNA damage prevention, electrolyzed water can also help to prevent damage to RNA and proteins (ascorbic acid). [5]
Using electrolyzed water for cleaning
In tests, strong acidic ionized water has been shown to reduce the levels of e-coli on spinach and lettuce below the detection limit, with the combination of strong alkalized water as pre-rinsing water. [6]
Many people use strong alkalized water to wash oil-based herbicides and pesticides off their fruits and vegetables. It has been shown to be effective, primarily for reducing pesticide residues. Also, tests have shown it is more effective than tap water or other detergents, without causing any loss in vitamin C or any other nutrients. [7] The main reason for this efficiency is its ability to emulsify oils and lipids.
Studies have also shown that the use of electrolyzed acidic water is also effective in reducing, and inactivating salmonella on Alfalfa seeds and other sprouts. [8] Also, being effective for reducing E. Coli and Salmonella from Mung Bean, broccoli, and radish seeds and sprouts. [9]
Effective for use as a mouthwash, or as a toothbrush disinfectant. [10] Many people who have used strong acidic water, and strong alkaline electrolyzed water have also noticed benefits for reduced plaque.
Also, from testing, strong acidic electrolyzed water has shown to exhibit a bacteriostatic/bactericidal effect against bacteria related to infected root canals. [11] Today, more dental offices are incorporating the use of this water for dental practices. Not only for cleaning and sterilizing medical equipment, but also for application processes.
The use of oxidizing electrolyzed water is very effective for removing E. Coli and L. monocytogenes from cutting boards, after soaking for 5 to 10 minutes. As acidic electrolyzed water has a positive ORP value, it has a high oxidizing effect. Strong acidic electrolyzed water can sometimes have a value of +1,200 or more. Measuring this high, it is able to destroy bacteria within 30 seconds of contact. Usually, 99% of pathogens die within about 5 to 10 seconds all depending on the oxidizing effect and power of the water.
Therefore, it has been concluded that the use of this water is an effective, safe cleaning method. [12]
The use of electrolyzed water has many benefits over other chemical cleaning agents: easy to operate, environmentally friendly, effective disinfection, and relatively inexpensive. Also, compared to hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, electrolyzed water is non-corrosive to the skin, mucous membrane, or organic materials. [13]
EOW (Electolyzed Oxidizing Water) applications for the skin
Chronic Ulcers:
Commonly, ulcers can be extremely difficult to heal. Electrolyzed strong acidic water is commonly used for skin conditions such as this in Asian countries, being especially popular in Japan.
It has been applied as a conservative treatment with satisfactory results. The affected area is usually soaked in a bowl for 20 minutes, or washed. Out of 15 different cases with infected ulcers, 7 have been healed, for 5 the infection subsided, and 3 were well granulated. A noticeable decrease in foul odor and discharge was apparent. The treatment of electrolyzed strong acidic water could then be conveniently utilized as the solution was found to be effective. [14]
Sanitizing the face and hands:
Conventional cleaners and disinfectants for the skin can have varying degrees of toxicity, which may cause skin irritation. Cleaning and disinfecting the skin with electrolyzed water overcomes many of these disadvantages involved with current skin cleaning methods. It is safer, lower in cost, less irritating, and more pathogenically effective. [15]
From conducted tests, it has been found that electrolyzed acidic water is highly efficacious, achieving higher disinfecting rates of harmful pathogens, compared to alternative cleaners. These tests performed by a major university, discovered that there was a 99.9999% reduction in Salmonella and E. Coli from on surfaces. Bacteria, viruses, spores, and molds are killed within seconds after application of this water. Unlike conventional cleaners and disinfectants, pathogens and bacteria are unlikely to become resistant to the use of electrolyzed water over time.[16]
General astringent purposes:
Acidic oxidizing water can be effective for use as an astringent on the face. Slight acidic electrolyzed water can be used to tone and tighten the face, as well as for anti-bacterial and cleaning purposes. As the skin has a slight acidic pH the use of acidic water can help to promote a proper balanced value of the pH. Also, with the oxidizing effect, it can help to send a signal to the skin cells to produce additional collagen for skin conditions related to skin wounds and conditions.
Currently the technology to produce electrolyzed water is well-utilized in many Asian countries, particularly in Japan where the use of it began over 4 decades ago. From many sources, it’s been said that between 15 to 20% of households utilize household water electrolysis units to produce water for consumption and cleaning purposes. Most of these sources have originated from Japanese studies. With the approval, in 1965, by the Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare, electrolyzed water is used commercially in places such as hospitals, restaurants, greenhouses, landscapes (golf greens, farm soils etc.), and health/fitness centers. Although awareness of this technology is currently lacking in western countries, it is slowly gaining increased attention as more and more people begin to incorporate electrolyzed alkaline and acidic water into their lifestyles.
About the author:
Shawn Butterworth has been studying alkaline water machines and the science behind the water they produce for over 3 years, and is an active advocate and promoter of its advantages for a healthier body and safer environment.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is for educational purposes only, and is not meant to provide substitute advice from a medical professional to treat, cure, alleviate, or prevent any kind of disease or condition. Quoted information is under the use of the ‘fair use policy’ to be used towards the overall education of others, to assist people to primarily understand the overall legitimacy of ionized water applications around the world.
[pro_ad_display_adzone id=”110027″]